Welcome to the A to Z of Bonsai.
We are compiling a worldwide A to Z of Bonsai database. The A to Z is written collaboratively by the people who use it and we would like to encourage anyone reading this page to contribute to what has become the worlds greatest encyclopedia of bonsai terms. Entries when they are made will be added to an editable list which will be checked prior to publication. Photos and images of the bonsai term can be added and links made to relevant web pages.
|
 - 42 entries - 42 entries |
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
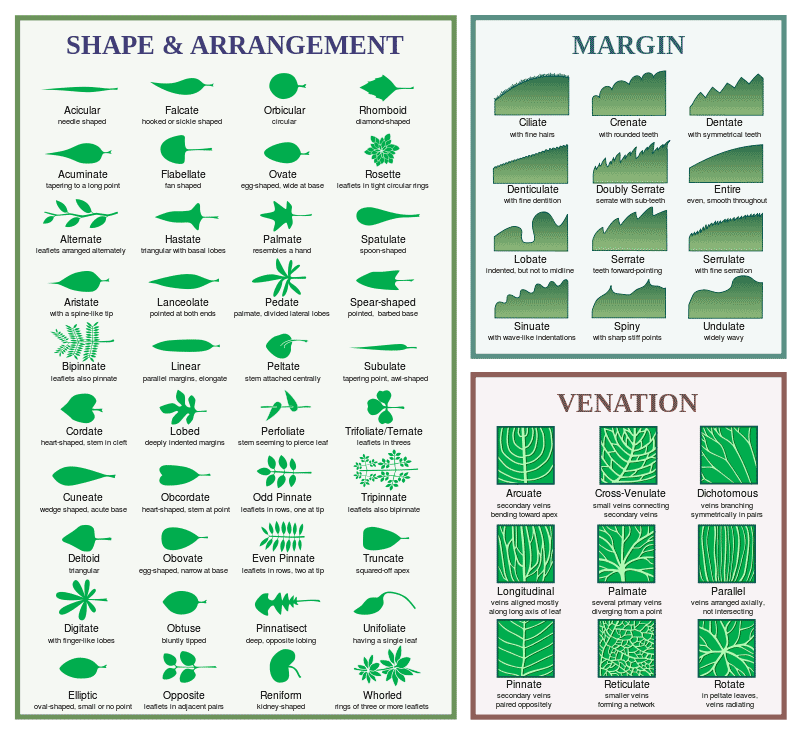
FALCATE (LEAF) - Refers to a leaf which is crescent or sickle SHAPEd, the curve being sideways.
|
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
CONESTYLE>FALLEN CONE STYLE - With hundreds of sprouts growing from one vicinity. In Japanese : Yama-yori.
|
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FASTIGIATE - Tree with erect branches set closely together (e.g. a Poplar)
|
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FASTIGIATUS - Branches erect and close together at ACUTE angle to the trunk e.g. hedging yew.
|
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FEATHERING - A process by which young saplings are allowed to retain their lower branches for a few years in order to thicken and strengthen the trunk. These branches are then removed in stages first CUTTING>CUTTING back the lowest in half, then in the following year removing them completely and cutting back the next lowest by half. This process is rePEATed until the clean trunk reaches the required height and GIRTH.
|
|
 |
|
|
   |

|
Feeder ROOTS - Those finer parts of the roots which collect the nutriets from the potting MEdium. Normally the fine roots at the ends of the thicker roots.
Part of the technique used in BONSAI>BONSAI>BONSAI is to encourage the growth of fine FEEDER ROOTS closer to the main TRUNK OF THE TREE. This is achieved by CUTTING>CUTTING back some of the main roots to stimulate new growth closer to the main trunk and may take place piecemeal over a number of REPOTTING sessions aCROSS a number of years..
Some planning and care must be taken in PRUNING>ROOT PRUNING to achieve the desired effect since the NEBARI of the bonsai tree is also a major consideration, and the main roots are also used naturally as support and anchorage for the tree.
|
| Thanks to - Kenny Middleton for use of the image |
|
 |
|
|
   |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FERNATIX - Supplier of miniature ferns suitable for accent or under planting. Sell by mail order but not on-line.
Write : Fernatix,
Stoke Ash,
Suffolk,
IP237EN
Email: mail@fernatix.co.uk
|
|
 |
|
|
   |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FERTILIZER - LIQUID - Acts more quickly than solids but heavy rain can FLUSH it through the soil quite quickly, so not giving the plant tiME to absorb the nutrients.
|
|
 |
|
|
   |

|
FERTILIZER - SOLID - Sold in powder, granule or block/cake form.
Applied to the surface they provide a gradual feed each tiME it rains and their visibility on the surface helps decide when a new application is necessary.
In order not to detract from the tree image or be eaten by birds, these fertilizers can be housed in specifically designed FERTILIZER BASKETS.
|
|
 |
|
|
  |

|
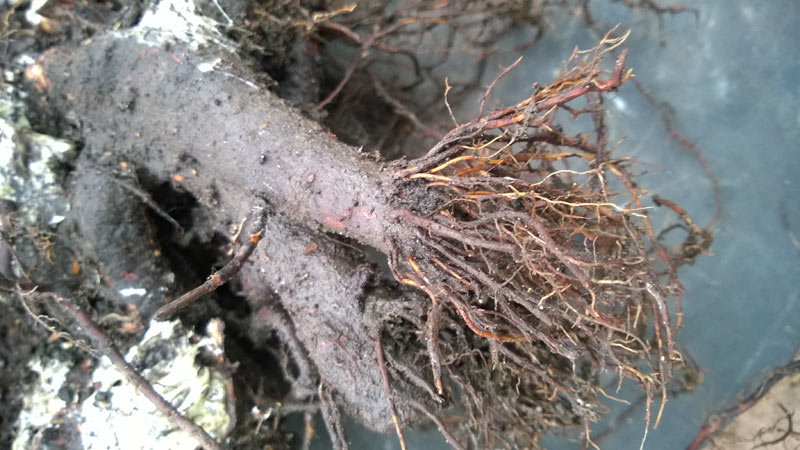
FERTILIZER BASKETS - Used to enclose solid fertilizer in order to prevent disturbance by birds.
Each tiME the tree is watered a portion of the fertlizer is washed through the soil.
There a number of designs : some (as illlustrated) are placed over the top of the solid fertilizer and some have lids on top and spikes on the bottom so that the fertilizer is self-contained while the spike keeps the basket firmly positioned in the soil.
|
| Thanks to - Green Dragon for use of the image |
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FIBROUS ROOT - A root system which contains many thin ROOTS as opposed to a single tap root.
|
|
 |
|
|
  |

|
FIELD MAPLE (ACER CAMPESTRE) - Small maple VARIETY native to Europe with fresh green, three lobed LEAVES in spring changing to bright yellow in autumn.
STYLE : Upright tree suitable for most styles except literati and are good for shohin sized speciMEns.
WARNING : Needs protection from scorching by exposure to the hottest summer sun. Also, small specimens require frost protection in winter.
|
|
 |
|
|
  |

|
BONSAI>BONSAI>BONSAISOCIETY>FIFE BONSAI SOCIETY - Fife Bonsai Society MEets on the 1st Friday each month 7pm to 9pm in Cupar Baptist Church Hall. 79 Bonnygate, Cupar, Fife KY15 4BY
Fife Bonsai Society website: http://www.fifebonsai.org.uk/
|
|
 |
|
|
  |

|
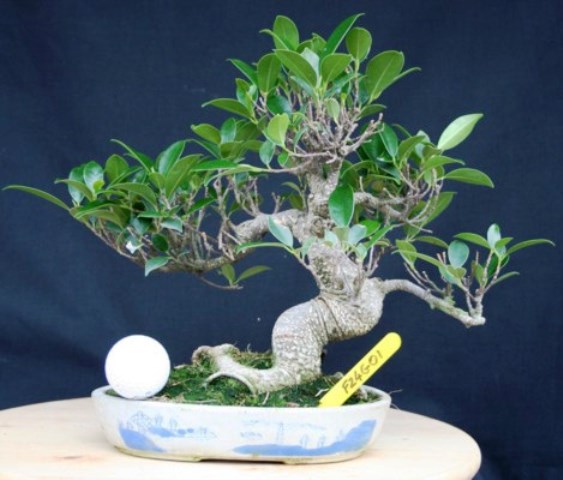
FIG (FICUS ) - Varieties used for BONSAI>BONSAI>BONSAI include : retusa and benjamina (WEEPING) in temperate climates and microcarpa and microphylla in warMEr araes. Originating from South East Asia and Australia, with leathery pointed oval LEAVES and aerial ROOTS, they are more closely related to the rubber plant than the large tree with edible FRUITs.
STYLE : Suited to all styles except literati and the aerial roots of the "banyan type" make them very good for root over rock.
WARNING : Figs dislike draughts or sudden changes in temperature or HUMIDITY.
|
| Thanks to - Green Dragon Bonsai for use of the image |
|
 |
|
|
   |

|
FIREBLIGHT - Fireblight is caused by a bacteria (Erwinia amylovora) which first attacks the blossoms progressing to the twigs and then the branches. FLOWERS turn brown and wilt; twigs shrivel and blacken, the ends often curling. In advanced cases discoloured oozing red/amber patches, form on branches. The translucent amber or reddish ooze (see image) contains masses of bacteria.
Most susceptable are : varieties of pear and apple trees (including crab apple), MOUNTAIN ASH, hawthorn and cotoneaster.
TreatMEnt involves sparaying shortly after BUD>BUD BREAK, with systemic FUNGICIDE. RePEAT the spray at one to two month intervals, more frequently in high disease situations.
Prune out infected branches 12 to 16 inches beyond the last visible signs of the disease on the branch. It is critical that the PRUNING tools be sanitized after each branch is pruned, so as to prevent spreading the disease form branch to branch.
|
| Thanks to - Wikipedia for use of the image |
|
 |
|
|
  |
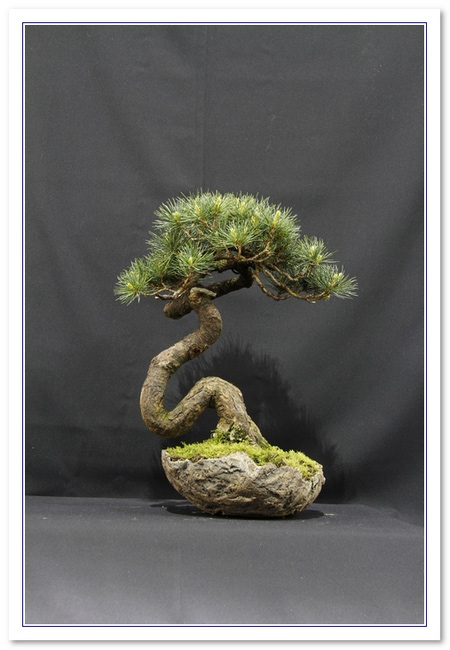

|
Five NEEDLE pine - SPECIES of Pine whose needles grow in clusters of five. Most common is white pine (Pinus Parviflora).
|
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FIVE TREE STYLE - A grouyp planting of 5 trees. In Japanese : GOHON-YOSE.
|
|
 |
|
|
   |
|
FLABELATE (LEAF) - Fan SHAPEd
|
| Thanks to - Wikipedia for use of the image |
|
 |
|
|
   |

|
BONSAI>BONSAI>BONSAI>FLIT BONSAI - Provides workshops and trees for sale and a re-potting service.
Web site offers information on the history of bonsai, different SPECIES and how to propagate them, and care of bonsai.
|
| Thanks to - Flit Bonsai for use of the image |
|
 |
|
|
  |
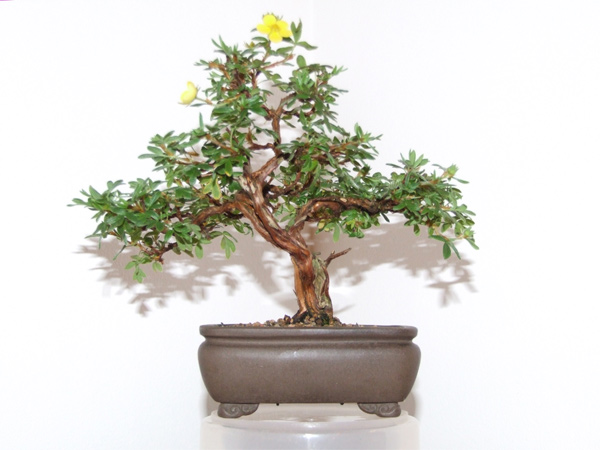

|
FLOWERS - Trees which normally flower as part of their reproduction process will flower when grown as a BONSAI>BONSAI>BONSAI.
The flower of the bonsai will reduce in size as the LEAVES of the tree/bush reduce in size although the size of the flower is not normally proportionate to the size of the reduced tree i.e. the flower seems disproportionately larger.
Flowers are the precursor to seed when the flower is pollinated. Flowers and seeds are soMEtimes left on the tree but sometimes they are removed. Some trees benefit from the removal of the flowers/seeds to direct most of the trees energy into producing wood and foliage.
|
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FLUSH - A surge of new growth . All trees produce a flush of LEAVES in spring, soME earlier than others and most, after a rest, will produce a second flush during mid-summer. (Note: certain pines are an exception).
|
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FLUTED - Describes the SHAPE of a trunk which has rounded vehicle grooves, usually emanating from the root buttress and going up the tree. Most common examples in the UK are Lombardy Poplar and hornbeam.
|
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FOLIAGE PAD - A mass of foliage on a branch, often referred to as a cloud.
|
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FOLIAR FEED - A fertilizer capable of being sprayed on and absorbed by the LEAVES/foliage.
|
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FORMAL UPRIGHT STYLE - With a straight vertical trunk and regular branch placeMEnt. Japanese name : CHOKKAN.
|
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FORSYTHIA (FORSYTHIA) - DECIDUOUS shrub bearing bright yellow FLOWERS on bare branches during spring which develop into dark green, lance-SHAPEd, serrated edged LEAVES in late spring/early sumMEr. It has pale brown BARK and a stiff and compact nature when pruned.
STYLE : Ideal for formal and informal upright, slanting, cascade and semi-cascade and group styles.
WARNING : None recorded.
|
|
 |
|
|
   |

|
BONSAI>BONSAI>BONSAIGROUP>FORTH VALLEY BONSAI GROUP - Club - Forth Valley Address -
Mayfield Centre,
FK7 0DB
Convenor - John Bannockburn. Tel No - 01295 731094 Email - rjohn-morris@lineone.net
MEetings - First Tuesday of the month 7.30pm
|
|
 |
|
|
  |

|
FRANK DOWLAT - A series of YouTube videos from AMErican BONSAI>BONSAI>BONSAIST>BONSAIST Frank Dowlat.
Explains many of the often asked questions about bonsai posed by people new to the hobby. The lectures are delivered in an informal and relaxed style but impart a wealth of bonsai experience.
|
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FRIABLE - Readily crumbled - with reference to soil
|
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FROND (LEAF) - A feather-like leaf such as those of ferns or palms.
|
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FRUIT - This is the part of the tree that contains its seed in the form of pods or berries.
|
|
 |
|
|
   |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FUCHSIA - There are approximatly 110 recognized SPECIES of Fuchsia mostly from South AMErica, but with some occurring up through Central America to Mexico, and also several from New Zealand to Tahiti. Small leaved varieties such as Mycrophylla and Tom Thumb and Lady Thumb are best for BONSAI>BONSAI>BONSAI.
STYLE : Suited for informal upright, cascade/semi-cascade, slanting and root over rock.
WARNING : Although they can be wired at any time, branches are brittle and easily snapped. Best WIRING time is winter after soil has been allowed to dry out a little, making branches a bit more flexible.
|
|
 |
|
|
   |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FUKIEN TEA (CARMONA MICROPHYLLA) - A tender, EVERGREEN shrub with buff to brown BARK bearing a dense CANOPY of shiny, dark green LEAVES and also tiny white FLOWERS all year round, if sufficiently high temperatures and HUMIDITY can be provided.
STYLE : Best suited to informal upright but prolific SHOOTS MEan that almost any SHAPE can be obtained.
WARNING : Will die if exposed to any frost at all.
|
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FUKINAGASHI - The windswept style of BONSAI>BONSAI>BONSAI. Although this is one of the most dramatic of all bonsai styles it is one of the most difficult to achieve convincingly.
|
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FUKINAGASHI KENGAI - Cascade with windswept branches or trunk
|
|
 |
|
|
   |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FUNGAL DISEASE - Virus infection exhibited by LEAVES or FLOWERS that are distorted or discoloured. Examples include MILDEW, RUST, BLACK SPOT and others.
|
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FUNGICIDE - A chemical used to control diseases caused by fungi.
|
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FUNGUS - A primitive form of plant life which is the most common cause of infectious diseases e.g. MILDEW/RUST.
|
|
 |
|
|
   |

|
FUNGUSGNATS>FUNGUS GNATS - Fungus gnats are small, dark, short-lived fliesthe larvae of which feed on plant ROOTS and fungi.
Fungus gnats are typically harmless to healthy plants but can inflict extensive damage to seedling. Their presence can also indicate more serious problems, particularly overWATERING; they may be feeding on roots that have sat in drain water too long and are thus rotting, or the gnats may be attracted to fungus growing in saturated topsoil. Consequently, allowing the soil to dry may reduce their numbers.
|
|
 |
|
|
   |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
FUSCHIA (FUSCHIA) - Shrub originating from South and Central AMErica now grown widely as garden and greenhouse plant for their colourful FLOWERS. Only small leaved varieties such as macrophylla are suitable for BONSAI>BONSAI>BONSAI.
STYLE : best suited to small/very small size specimens in informal upright, cascade, semi-cascade, slanting and root-over-rock styles.
WARNING : Branches can be brittle and snap easily.
|
|
 |
|
|
  |
(No Photo Yet)
(Send Image) |
BUD>BUD)>FUSIFORM (BUD) - Describes the SHAPE – usually of a bud – which is wider in the centre than at either end.
|
|
 |
|
|
   |
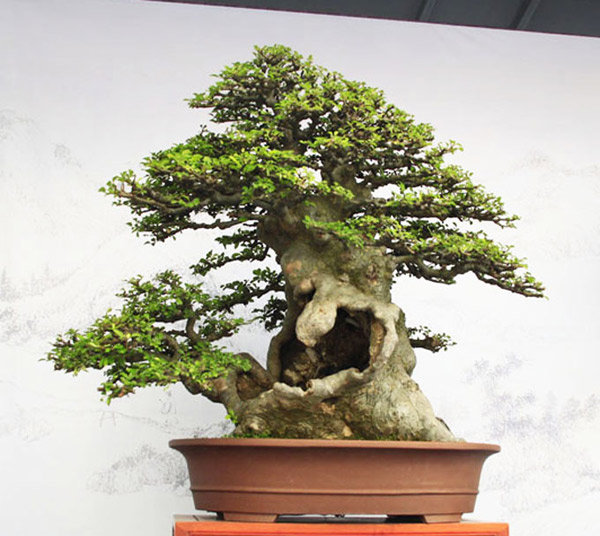

|
Futo-MIKI - Giant, or grotesque trunk.
|
| Thanks to - Courtesy of Robert Steven (sent from BCI convention in China published by Bonsai Bark) for use of the image |
|